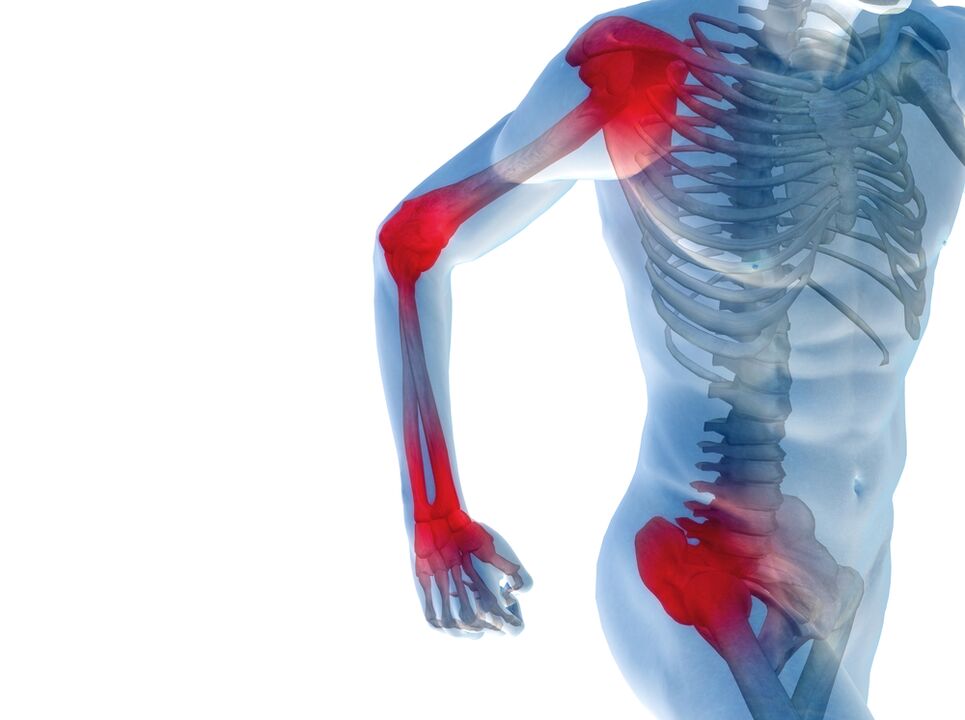
Prevalence of joint pain
Arms and legs undergo significant stress throughout life—weight, movement, injuries. Joint pain, soreness and deformation are inevitable with age-related changes in the musculoskeletal system.
pain mechanism
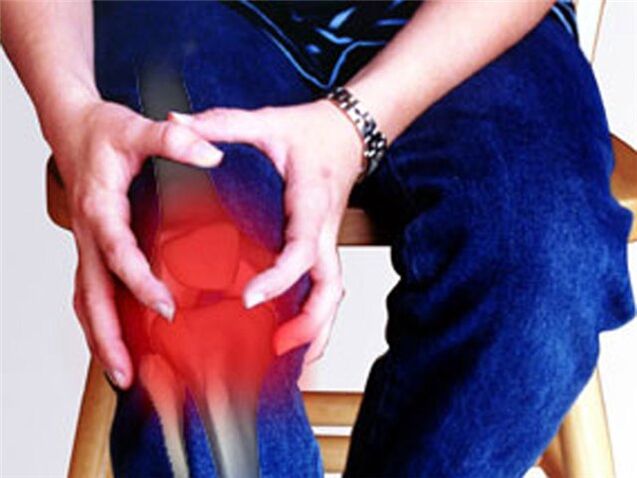
- Joint inflammation or polyarthritis.Inflammation itself triggers the production of pain-causing substances. Additionally, they increase the sensitivity of pain receptors to repeated exposure. This is why the usual load on an inflamed joint results in a severe pain response.
- Swelling of joints.It increases in size and looks like a joint tumor. Edematous tissue mechanically exerts pressure on joint structures, causing discomfort and exacerbating the severity of the process.
- Changes in malnutrition.This can be called wear and tear of bones and cartilage. With age and continued stress, joint function deteriorates. The production of synovial fluid is disturbed and sliding of the joint surfaces becomes difficult. They stimulate the growth of subchondral bone through constant stimulation through friction. This type of marginal bone growth is called osteophytes and can cause real pain. They look like raised bumps on the joints. Osteophytes are often injured, which causes inflammation, completing the pathological cycle.
- Trauma and post-traumatic complications.Serious injuries: Bruises, dislocations, broken bones will not go away and leave no trace. Even if the injury heals, joint pain and stiffness may remain with you for the rest of your life. Doctors often encounter complaints of pain in damaged joints. The situation usually gets worse when the weather changes or at night.
- Exchange barriers.Calcific deposits in tendons and ligaments due to metabolic disorders. Their violation can lead to severe pain syndrome.
These pathological processes in the joints develop in diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Musculoskeletal system diseases
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis affects any joint, regardless of size. The only thing that matters is that they take enough pressure.
- constant load. It may be redundant or monotonous. Static loading plays an important role in the development of joint changes.
- Hypothermia or overheating.
- Injuries – Bruises, fractures, subluxations and dislocations.
- excess weight. Obesity is one of the most important risk factors for developing osteoarthritis.
- Malnutrition.
- lack of exercise.
- Infection and subsequent joint inflammation is polyarthritis.
shoulder girdle degenerative disease

- Deposition of calcification in the supraspinatus tendon and the resulting painful abducens arc syndrome. In this pathological condition, joint pain occurs when trying to move the shoulder along a certain arc. If you change the angle of inclination, the pain disappears.
- Frozen shoulder syndrome. This condition is characterized by severe stiffness in the shoulder girdle. Occurs due to prolonged immobilization of the shoulder - provide rest to the arm suffering from thoracic radiculitis when using a bandage.
No significant deformation of the shoulder strap elements was observed. Symptoms and complaints related to injury to adjacent structures, rather than deforming osteoarthritis of the shoulder, are usually the first to appear.
elbow osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis deformans of the elbow is common in tennis players, masons and miners, blacksmiths and foundry workers.
Osteoarthritis of hand and finger joints
- The number of professions that put pressure on hands and finger joints is increasing - programmers, typists and simple computer users. And most young people are involved.
- Work in low temperature conditions. They are winter tram and trolley bus drivers, builders and villagers.
- The knuckles lack normal dynamic loading. Few people make the effort to do gymnastics, especially therapeutic exercises.
- Accompanying disease - joint inflammation.
degenerative foot disease
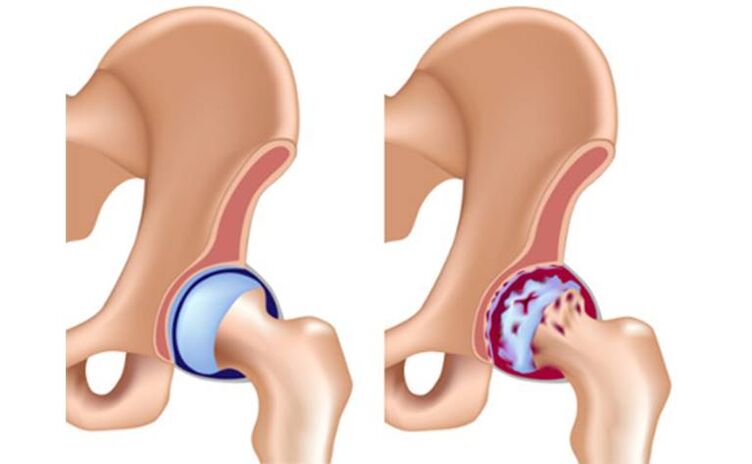
- Hip Injuries – Hip Arthrosis.
- Injury to the knee and development of knee arthrosis.
- Dystrophic diseases of the feet.
Hip arthrosis
Joint pain can be excruciating, debilitating, and bother you at any time of the day. In the morning, my movement is limited and I have to work on my hip joints to get them apart.
knee joint disease

At first they are found only in the thickness of cartilage, then on its surface, in joint cavities, tendons and even muscles.
dystrophic changes in foot joints
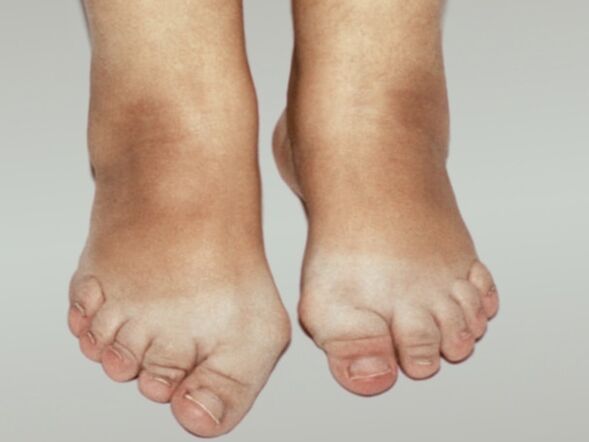
Inflammatory diseases of the musculoskeletal system
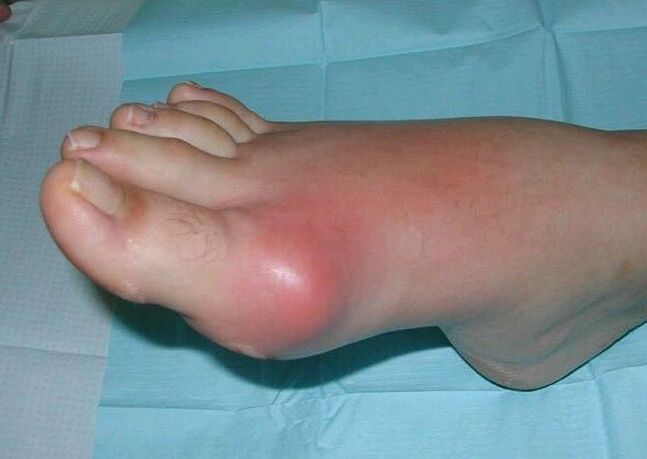
- joint pain.It's usually acute - a burn or a shot. If the cause of arthritis is an infection, the inflammation becomes purulent. In this case, the pain will be throbbing and very intense. In chronic and subacute forms, joint pain resembles variants of arthropathy.
- Change shape.In the acute course, inflammatory tumors form in the joint area, the color of the skin changes, and the temperature increases. If a bacterial infection occurs, the usual symptoms of poisoning occur - high fever, chills, a sharp deterioration in health. For people with polyarthritis, the disease can be especially difficult to live with.
- Impaired function.Movement of the inflamed joint is significantly limited due to pain and fluid accumulation in the joint cavity. This swelling acts like an inflammatory tumor and mechanically prevents movement.
causes of arthritis
- Contagious.This condition occurs when a joint is directly affected by an infection, such as Lyme disease. Infections can be viral or bacterial, penetrating from the outside or affected adjacent organs, bones. Arthritis caused by bacterial infections is particularly serious.
- reactive.In this case, the inflammatory process is a response to a past or current infection. These include damage to the musculoskeletal system following influenza, colds, and genitourinary infections. An important sign is a link to infection.
- self-immune.Sometimes, a person's immune system begins to destroy its own cells. Manifestations of this disease vary, but joint syndrome is usually the most obvious manifestation. The most common autoimmune pathology is rheumatoid polyarthritis. It is characterized by severe joint deformation accompanied by persistent pain.
There is no cure for autoimmune polyarthritis, but treatment must be discontinued to control the disease in its early stages.
Treatment of joint diseases

ethnoscience
Folk remedies are diverse, but you need to remember that they can only treat minor illnesses and must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
drug

- Analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs.Usually these are drugs from the same group. Since the main symptom of joint disease is pain, pain relief is a doctor's top priority. Good results can be achieved using topical treatments.
- Steroid hormones and cytostatics.It is strictly forbidden to take these medications without a doctor's prescription. They are used in all serious autoimmune processes and are designed to relieve specific inflammation in the body. Without hormonal drugs, it is impossible to get rid of the pain and inflammatory tumors of rheumatoid polyarthritis. They also inhibit joint deformation.
- antibiotic.These medications are needed if the cause of your arthritis is a bacterial infection. The broad-spectrum antibiotics used penetrate well into bone tissue. Sometimes, doctors may use several groups of antibiotics to treat the infection if the pathogen persists. This is also reasonable if the disease is caused by mixed infections. It is important to remember that antibiotics are powerful drugs with individual side effects, and it is necessary to strictly follow the doctor's instructions during treatment.
- Preparation to protect and restore cartilage.Treatment of chronic polyarthritis and deforming osteoarthritis is impossible without chondroprotectants. For this purpose, single drugs (chondroitin or glucosamine) and combination drugs can be used. There is an extensive evidence base for the use of chondroprotectants based on many clinical trials.
- Intra-articular injection.This is the best way to deliver drugs directly to the site of disease. Typically, hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs are injected into the joint space. In recent years, hyaluronic acid has also been used for intra-articular injection.
physiotherapy

Orthopedic devices are also used to limit movement of the affected joints. These include orthotics and splints. The purpose of these devices is to reduce the load on diseased joints.































